How to Handle Tooth Decay? 5 Stages from Early Symptoms to Severe Tooth Decay, Plus Prevention and Treatment Methods

What is Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay (also known as cavities) refers to the gradual loss of tooth enamel caused by bacterial erosion, leading to the formation of holes. When bacteria in the mouth break down the sugars in food debris, acidic substances are produced, which damage the tooth’s protective layer and cause the tooth structure to gradually deteriorate. If left untreated, tooth decay can spread from the enamel to the dentin and even reach the pulp, resulting in severe pain and, in some cases, tooth death or loss.

Causes of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is primarily caused by a combination of factors, including bacteria in the mouth, eating habits, oral hygiene, and individual tooth structure. When these factors continuously affect the teeth, the enamel gradually erodes, eventually leading to the formation of cavities. Below are detailed explanations of several major causes:
Bacterial Activity in the Mouth
The mouth naturally contains a large number of bacteria, some of which combine with food debris to form dental plaque. After eating, especially sugary or carbohydrate-rich foods, these bacteria break down the sugars and produce acidic substances. These acids gradually erode the enamel on the tooth surface, leading to calcium loss and the formation of cavities. If left unchecked, bacteria will continue to erode the tooth, causing cavities to enlarge over time.
Dietary Habits
Diet plays a significant role in tooth decay, particularly when consuming high-sugar and acidic foods, such as:
- High-sugar foods: Candies, chocolates, pastries, and soft drinks contain large amounts of sugar, providing nutrients for bacteria to produce more acid, which accelerates enamel demineralisation.
- High-acid foods: Citrus fruits, vinegar, and other acidic foods directly soften enamel, making teeth more susceptible to bacterial erosion.
- Frequent snacking: Constantly eating snacks or drinking sugary beverages keeps the mouth in an acidic environment for extended periods, preventing teeth from naturally repairing themselves and increasing the risk of cavities.
Inadequate Oral Hygiene
Failing to brush and floss properly every day allows food debris to remain on the tooth surface or between teeth, leading to plaque formation. Over time, plaque hardens into tartar, providing a breeding ground for bacteria. These bacteria produce acids that accelerate tooth decay. Therefore, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for preventing cavities.
Insufficient Saliva Production
Saliva plays a crucial protective role in the mouth by:
- Neutralising oral acidity to reduce acid damage to teeth.
- Washing away food debris to minimise bacterial growth.
- Promoting remineralisation to repair early-stage enamel demineralisation.
When saliva production decreases due to factors such as lack of sleep, stress, certain medications (e.g., antihistamines, antidepressants), frequent smoking, or alcohol consumption, the mouth’s natural defence system weakens, increasing the risk of cavities.
Tooth Alignment Issues
Crowded, misaligned, or improperly aligned teeth can create hard-to-clean areas, particularly in deep gaps or overlapping regions. These spots tend to trap plaque and food debris, increasing the likelihood of cavities. Orthodontic treatments, such as clear aligners, can help improve tooth alignment and reduce the risk of tooth decay.
Protect Your Teeth Now! Dental Check-ups Help Detect Problems Early!
Tooth decay is a common dental issue, but with proper care and early treatment, it can be effectively managed to maintain healthy teeth. Whether it’s a minor cavity or deep decay, addressing it early can prevent the need for more complex dental procedures.
🔹 Have you been experiencing tooth sensitivity or pain lately?
🔹 Worried that cavities may be affecting your oral health?
🔹 How long has it been since your last dental check-up?
Now is the best time to protect your teeth! Regular dental check-ups help detect problems early, preventing cavities from worsening and keeping your teeth strong and healthy.
💡 Take action now! Schedule a professional dental check-up with our expert dental team for personalised care and advice to ensure your oral health remains in top condition!
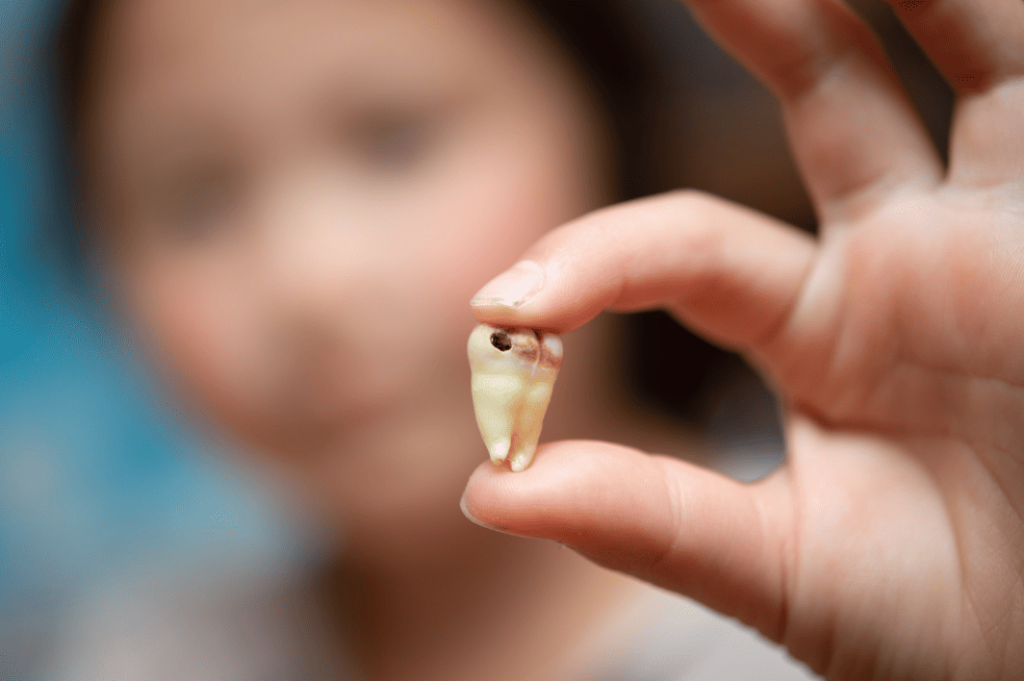
Different Stages of Tooth Decay and Their Severity
Tooth decay is a progressive condition that starts with the demineralisation of enamel and can eventually lead to damage in the dentin, pulp, and even the tooth root. If left untreated, cavities will continue to worsen, potentially resulting in tooth loss or requiring root canal treatment. Below is a breakdown of the different stages of tooth decay and their associated symptoms:
Early Stage of Tooth Decay (Enamel Demineralisation)
At the initial stage, bacteria-produced acids gradually erode the enamel, leading to mineral loss on the tooth surface. At this point, there is usually no significant pain, but some minor changes may occur, such as:
- The appearance of white or light yellow spots on the tooth surface (early demineralisation signs).
- Mild sensitivity to hot or cold foods, such as discomfort when drinking cold water or eating sweets.
- Occasional mild toothache, usually not persistent, but discomfort may arise when chewing harder foods.
👉 This stage is the easiest to reverse. Remineralisation through fluoride treatments and improved oral hygiene can help repair early decay.
Middle Stage of Tooth Decay (Dentin Damage)
As decay progresses, bacteria penetrate the enamel and start attacking the dentin (the layer beneath the enamel). At this stage, the following symptoms may occur:
- Visible dark spots or small holes on the tooth surface, often appearing on molars’ biting surfaces or between teeth.
- A dull ache or short bursts of pain while eating, especially when consuming sweet or cold foods.
- Occasional bad breath, as bacteria break down dentin, leading to an unpleasant odour.
👉 At this stage, visiting a dentist promptly is crucial. The cavity can typically be treated with a dental filling to prevent further deterioration.
Advanced Tooth Decay (Pulp Involvement)
Once bacteria reach the pulp, the nerves become affected, leading to significant and persistent pain. The symptoms of severe tooth decay include:
- Increased and prolonged toothache, particularly at night, possibly interfering with sleep.
- Sharp pain when consuming hot or cold foods, indicating nerve infection.
- Possible gum inflammation or swelling, and in severe cases, facial swelling.
👉 At this stage, a simple filling is no longer sufficient. A root canal treatment may be required to remove the infected nerve tissue, preventing the spread of infection.
Severe Root Infection (Possible Need for Root Canal Treatment)
When infection spreads to the tooth root, it affects not only the pulp but also the surrounding gums and jawbone, leading to more severe symptoms:
- Tooth discolouration, turning dark yellow or grey, indicating nerve death.
- Swollen, red gums with possible pus discharge; in severe cases, the infection can spread to nearby teeth, causing gum abscesses or even cellulitis.
- Loose teeth with a risk of falling out; in extreme cases, extraction may be necessary.
👉 At this stage, root canal treatment or even tooth extraction may be required. In cases of tooth loss, dental implants or bridges may be considered to restore chewing function.
*Tooth decay progresses from mild to severe, with each stage presenting different symptoms and requiring different treatment approaches. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce discomfort and prevent tooth loss. Regular dental check-ups are recommended, and any early signs of decay should be addressed promptly by a professional dentist.
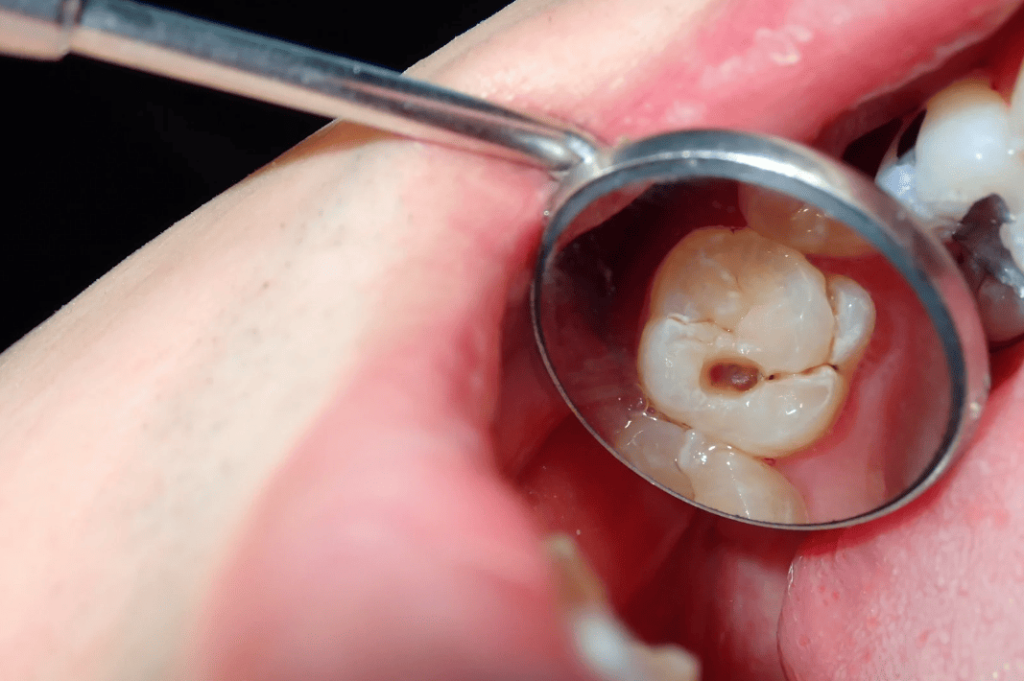
How to Identify and Address Different Stages of Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is a progressive condition that often goes unnoticed until pain arises. Understanding the different stages of tooth decay and taking appropriate action can help minimise damage and even reverse decay in its early stages.
Self-Detection Methods
You can check for signs of tooth decay using these simple methods:
🔍 Regularly Check Your Teeth in the Mirror
- Observe any white or light yellow spots on your teeth, which may indicate early-stage demineralisation.
- Look for black spots, dark lines, or visible cavities, which are signs of advanced decay.
👃 Check for Unusual Odours or Sensitivity
- If you notice bad breath upon waking up or after long periods without eating, it may be due to tooth decay or bacterial buildup.
- If your teeth feel sensitive to cold, hot, sweet, or acidic foods, it could be a sign of enamel damage.
👅 Feel the Surface of Your Teeth with Your Tongue
- If certain areas feel rough or uneven, it may be an indication of enamel erosion or cavity formation.
💡 If you suspect tooth decay, visit a dentist as soon as possible to prevent further deterioration!
The Importance of Dental Check-Ups
Even with self-examination, some cavities are not easily visible. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for detecting hidden decay.
🦷 Professional Diagnosis Detects Hidden Cavities
- Dentists use magnifying tools and probes to identify early signs of decay with greater accuracy.
- Some cavities develop between teeth or inside the tooth structure, making professional assessment necessary.
📸 Dental X-Rays Reveal Hidden Tooth Decay
- X-rays provide a detailed view of internal tooth structures, helping detect cavities between teeth and near the roots.
- Dentists may recommend an X-ray every 6–12 months to monitor hidden decay.
👨⚕️ Personalised Care Advice from Your Dentist
- Based on your dietary habits, cleaning routine, and dental structure, a dentist can offer tailored oral care recommendations.
- If you have crowded teeth, braces, or dental bridges, your dentist can provide specific guidance on cleaning techniques to reduce cavity risks.
💡 Regular dental check-ups every 6–12 months can help prevent problems before they start, even if you don’t experience symptoms!
Treatment Options Based on Severity
Once decay is confirmed, the appropriate treatment depends on the severity of the condition.
🟢 Early Stage (Enamel Demineralisation)
- Improve oral hygiene by brushing twice daily, focusing on areas prone to cavities, such as molars and between teeth.
- Use fluoride toothpaste or dentist-recommended fluoride treatments to aid enamel remineralisation and reverse early decay.
- Reduce consumption of high-sugar foods (e.g., sweets, soft drinks) to prevent bacteria from producing acids that accelerate decay.
🟡 Moderate Stage (Dentin Damage)
- Dentists typically perform dental fillings using materials like composite resin, ceramic fillings, or amalgam to restore the tooth’s shape and function.
- If sensitivity persists, desensitising treatments may be required to reduce discomfort from hot and cold foods.
- Maintain good oral hygiene to prevent further cavities in other areas.
🔴 Severe Stage (Pulp or Root Infection)
- If decay reaches the pulp, root canal treatment (endodontic therapy) is necessary to remove infected pulp tissue and restore the tooth with a crown.
- In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, tooth extraction may be required. The missing tooth can be replaced with dental implants or bridges.
- If gum inflammation occurs, antibiotic treatment or periodontal care may be necessary to control infection.
💡 The earlier tooth decay is detected, the simpler and more cost-effective the treatment. Early intervention leads to better recovery outcomes!
Treatment Methods for Tooth Decay
The treatment for tooth decay depends on its severity. From simple fillings to more complex root canal treatments or even extractions, each method aims to restore the health and function of the affected tooth. Below are the main treatment options for different stages of tooth decay.
1. Dental Fillings
When tooth decay is in the early stages, mainly affecting the enamel or dentin, dentists use fillings to repair the damaged area and prevent further deterioration.
Treatment Process
- Local anesthesia may be used, depending on the case, to ensure a painless procedure.
- The dentist removes the decayed portion of the tooth using professional tools, ensuring no infected tissue remains.
- The cavity is filled with materials such as composite resin, porcelain, or amalgam to restore the tooth’s shape and function.
- The filling is adjusted to fit naturally with the surrounding teeth, preventing bacterial reinfection.
Best for
- Minor tooth decay that has not reached the tooth’s nerve.
- Teeth with enough healthy structure to support a filling.
Things to Note
- Temporary sensitivity to hot and cold foods may occur but usually improves within a few days.
- Avoid chewing hard foods immediately after the procedure to prevent the filling from loosening.
2. Root Canal Treatment
When tooth decay reaches the inner part of the tooth and affects the pulp (nerve tissue), it can cause severe pain and sensitivity to hot and cold. In such cases, a root canal treatment is required.
Treatment Process
- The dentist administers local anesthesia to ensure a painless procedure.
- The infected pulp is removed, and the root canal is thoroughly cleaned to eliminate bacteria and dead tissue.
- The canal is disinfected and filled with gutta-percha or other biocompatible materials to prevent reinfection.
- A dental crown may be recommended to protect the weakened tooth.
Best for
- Teeth with severe decay causing intense pain.
- Inflamed or dead pulp that affects overall dental health.
Things to Note
- After a root canal, the tooth becomes more fragile, so a crown is often needed for protection.
- Mild discomfort may persist for a few days after treatment.
3. Dental Crowns
When tooth decay is extensive and a regular filling is insufficient, a dental crown may be needed to cover and protect the tooth while restoring its function.
Treatment Process
- The dentist reshapes the tooth to accommodate the crown.
- An impression or digital scan is taken to create a custom-made crown.
- A temporary crown may be placed while waiting for the permanent one.
- The permanent crown is fitted and adjusted to ensure a natural bite.
Best for
- Teeth that have undergone root canal treatment and need reinforcement.
- Teeth with extensive decay that cannot be restored with fillings alone.
- Damaged but salvageable teeth that do not require extraction.
Things to Note
- It may take a few days to get used to the crown.
- Good oral hygiene is essential to prevent bacteria from accumulating around the edges of the crown.
4. Tooth Extraction
When tooth decay has severely damaged the tooth structure, making it impossible to restore, extraction may be necessary to prevent further infection and complications.
Treatment Process
- The dentist administers local anesthesia to ensure a painless procedure.
- Special instruments are used to loosen and remove the tooth. If the tooth is deeply rooted or broken, surgical extraction may be required.
- Gauze is placed over the socket to control bleeding and promote healing.
- The dentist may prescribe antibiotics or pain relievers to prevent infection and manage discomfort.
Best for
- Teeth that are too decayed to be repaired.
- Severe root infections that cannot be resolved with root canal treatment.
- Teeth with extensive structural damage that cannot support a crown or other restorations.
Things to Note
- Avoid drinking through a straw or rinsing vigorously after extraction to prevent dry socket.
- Follow post-extraction care instructions for proper healing.
- If the missing tooth affects chewing or appearance, consider dental implants or bridges as replacement options.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay?
Preventing tooth decay relies on good oral hygiene habits, healthy dietary choices, and regular dental check-ups. By following the right methods, you can effectively reduce the risk of cavities and maintain healthy teeth.
Proper Brushing Habits
Good brushing techniques are the foundation of cavity prevention, helping to remove plaque and reduce bacterial growth.
✔ Brush your teeth twice a day – It is recommended to brush in the morning and before bed for at least two minutes each time to ensure thorough cleaning of the tooth surfaces and between teeth.
✔ Use fluoride toothpaste – Fluoride helps strengthen enamel, reducing the risk of acid erosion and cavity formation.
✔ Choose a soft-bristled toothbrush – Avoid using hard-bristled brushes, as they may damage enamel or gums, leading to gum recession or tooth sensitivity.
✔ Master the correct brushing technique – The Bass brushing technique is recommended, where the toothbrush is held at a 45-degree angle to the teeth and gently brushed along the gum line and tooth surface to achieve comprehensive cleaning.
Using Dental Floss and Mouthwash
Brushing alone cannot completely remove plaque, so floss and mouthwash should be used to enhance oral care.
✔ Floss removes food particles between teeth – The spaces between teeth are prone to bacterial buildup. Using dental floss can effectively reduce the risk of cavities and gum disease. It is recommended to floss at least once a day, especially before bedtime.
✔ Fluoride mouthwash helps reduce bacteria – Fluoride mouthwash provides additional enamel protection and reduces bacterial growth, lowering the risk of cavities and gum inflammation.
✔ Avoid over-reliance on mouthwash – Mouthwash should not replace brushing and flossing but should be used as a supplementary tool for oral hygiene.
Dietary Control
Diet has a direct impact on oral health. Certain foods can accelerate the formation of cavities, so maintaining good dietary habits can significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay.
✔ Reduce sugar intake – Sugar is the main source of acid-producing bacteria. Excessive consumption of sweets, cakes, and chocolates increases the risk of cavities.
✔ Avoid carbonated drinks and acidic foods – Beverages like soda and fruit juices contain high acidity, which erodes enamel and makes teeth more vulnerable to decay. If consumed, it is advisable to use a straw to minimize contact with teeth.
✔ Rinse with water after meals – After consuming sugary or acidic foods, rinsing with water helps wash away food particles and acids, reducing tooth damage.
✔ Consume foods that promote oral health – Dairy products (milk, cheese), vegetables, and calcium-rich foods help strengthen teeth and lower the risk of cavities.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Even if there are no visible signs of tooth decay, regular dental visits are essential to detect issues early and receive proper treatment.
✔ Visit the dentist every six months – Regular check-ups help identify early-stage cavities, preventing them from worsening to the point of requiring root canal treatment or extractions.
✔ Professional teeth cleaning – Dentists or dental hygienists can remove tartar and plaque buildup through professional cleaning, preventing cavities and gum disease.
✔ Personalized oral care advice – Based on individual oral health conditions, dentists can recommend suitable preventive measures such as fluoride treatment or bite adjustment to further reduce the risk of cavities.
With good daily oral care and professional check-ups, you can effectively prevent tooth decay and maintain healthy teeth!
Protect Your Teeth Now! Dental Check-ups Help Detect Problems Early!
Tooth decay is a common dental issue, but with proper care and early treatment, it can be effectively managed to maintain healthy teeth. Whether it’s a minor cavity or deep decay, addressing it early can prevent the need for more complex dental procedures.
🔹 Have you been experiencing tooth sensitivity or pain lately?
🔹 Worried that cavities may be affecting your oral health?
🔹 How long has it been since your last dental check-up?
Now is the best time to protect your teeth! Regular dental check-ups help detect problems early, preventing cavities from worsening and keeping your teeth strong and healthy.
💡 Take action now! Schedule a professional dental check-up with our expert dental team for personalised care and advice to ensure your oral health remains in top condition!
Frequently Asked Questions About Tooth Decay
What should I do if I discover a cavity?
If you suspect you have a cavity, book a dental check-up as soon as possible to prevent it from worsening. Your dentist will recommend the appropriate treatment based on its severity, such as fillings, root canal treatment, or other restorative procedures.
How can early-stage cavities be treated?
If a cavity is still in its early stages (affecting only the enamel), using fluoride toothpaste and maintaining good oral hygiene can slow its progression. Regular dental check-ups help monitor the condition and prevent further damage.
Can a cavity heal on its own?
No, cavities do not heal on their own. Unlike bones, teeth cannot regenerate once damaged. If left untreated, cavities will continue to worsen, requiring professional treatment to restore tooth health.
How can I prevent cavities in children?
Children are more prone to cavities due to thinner enamel. Preventive measures include:
✔ Teaching proper brushing habits from an early age using fluoride toothpaste
✔ Limiting sugary foods and drinks to reduce acid attacks on teeth
✔ Scheduling dental check-ups every six months to detect and treat cavities early
✔ Considering fluoride treatments or dental sealants to protect against decay
If I don’t have tooth pain, does that mean I don’t have cavities?
Not necessarily! Many early-stage cavities do not cause pain, and by the time discomfort appears, decay may have already reached deeper layers of the tooth. Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection and prevention.
Why do I still get cavities despite brushing daily?
Cavities can form due to several factors, including:
🔹 Improper brushing technique, leaving plaque behind
🔹 Not flossing, allowing food particles to accumulate between teeth
🔹 Frequent consumption of sugary foods and acidic drinks
🔹 Low saliva production (dry mouth), reducing the mouth’s natural cleansing ability
Can cavities recur after a filling?
Yes, if oral hygiene is poor, decay can develop around fillings. Maintaining good oral care and having regular dental check-ups ensure that fillings remain intact and prevent further decay.
Will my tooth become weaker after a root canal treatment?
A tooth that has undergone root canal treatment loses its nerve and blood supply, making it more brittle. To protect it from fractures, a dental crown is often recommended for added strength and durability.
Do all cavities need to be filled, or can they be monitored?
It depends on the severity. If only the enamel is affected, fluoride treatments may slow or halt decay. However, once a cavity forms a hole, a filling is necessary to prevent further damage and the need for more extensive treatment.
Does tooth sensitivity mean I have a cavity?
Tooth sensitivity can be an early sign of a cavity but may also be caused by gum recession, enamel erosion, or other dental conditions. If you experience persistent sensitivity, consult a dentist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Disclaimer
All information provided on this website is for informational purposes only and is intended to help readers gain general knowledge about dental health. The content on this website should not be considered a substitute for professional dental diagnosis, advice, or treatment. If you have any dental concerns, please consult a licensed dentist for appropriate medical advice and treatment.
While we strive to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the information provided, we do not guarantee that all content is always up-to-date or applicable to individual circumstances. Smith & Jain Dentists and its affiliates are not responsible for any direct or indirect damages resulting from the use of this website’s information.
This website may include links to external websites for reference purposes only. Smith & Jain Dentists is not responsible for the content or accuracy of third-party websites.

Smith & Jain Dentists - Your Trusted Dental Care!
Our expert team is here for emergency and routine care to keep your smile healthy. Call or WhatsApp us today!