【2026 Guide to Gum Disease】Cost, Symptoms, and Causes Explained
Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease) is often called the “silent killer” of teeth. Many people in Hong Kong mistake bleeding gums for “heatiness” or brushing too hard, unaware that these are early warning signs of infection. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to receding gums, loose teeth, and eventually, total tooth loss.
This guide provides the 2026 latest treatment costs, a 30-second self-test, and a deep dive into the causes and stages of the disease. We also explain the critical difference between “Regular Scaling” and “Deep Cleaning” to help you protect your smile.
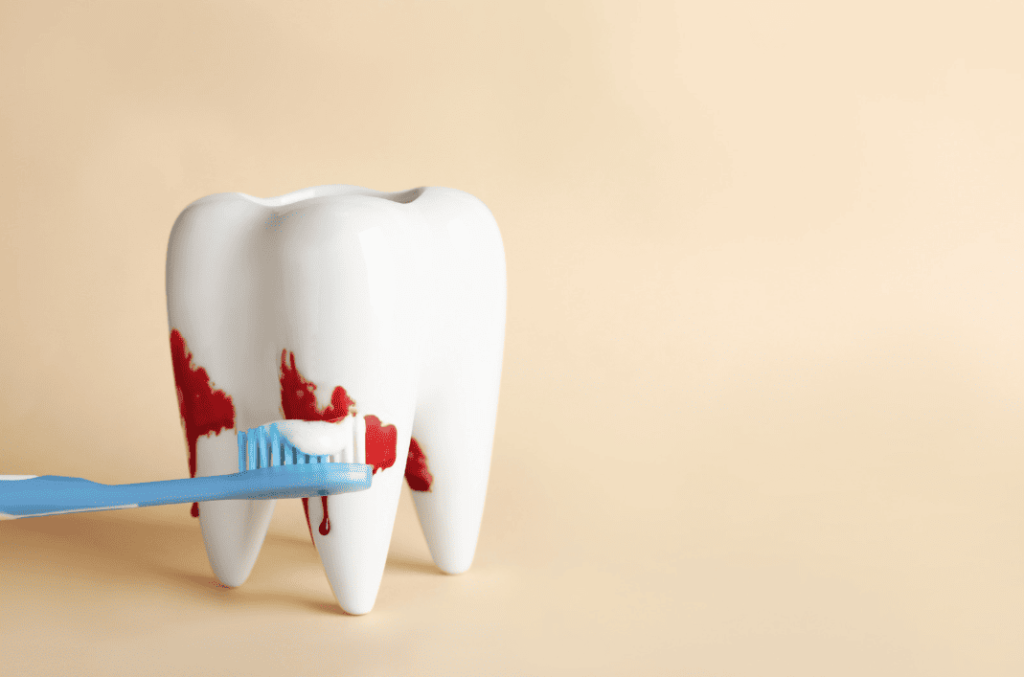
30-Second Self-Test: Do You Have Early Signs of Gum Disease?
In its early stages, gum disease is often painless and easy to ignore. Take 30 seconds to check if you have any of the following symptoms:
- [ ] Gums bleed during brushing or flossing (The most common early warning sign)
- [ ] Red, swollen, or tender gums (Healthy gums should be firm and pale pink)
- [ ] Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth that won’t go away
- [ ] Receding gums, making your teeth look longer or causing sensitivity
- [ ] Developing gaps between teeth where food frequently gets stuck
- [ ] Loose or shifting teeth, or a change in how your teeth fit together when you bite
- [ ] Pus appearing between your teeth and gums (Periodontal abscess)
Your Results:
- 1-2 Items: You may have early-stage Gingivitis. We recommend booking a professional cleaning and check-up as soon as possible to reverse the condition.
- 3 or More Items: You may have progressed to Periodontitis (moderate to severe gum disease). It is critical that you seek professional dental assistance immediately to prevent tooth loss.

The Pathology of Gum Disease: Why Do Teeth Fall Out “Silently”?
Many patients are confused: “Why are my teeth loose even though I have no cavities?” The reality is that gum disease is not a problem with the tooth itself, but a structural failure of the support system.
Understanding Damage Through “Foundation Collapse”
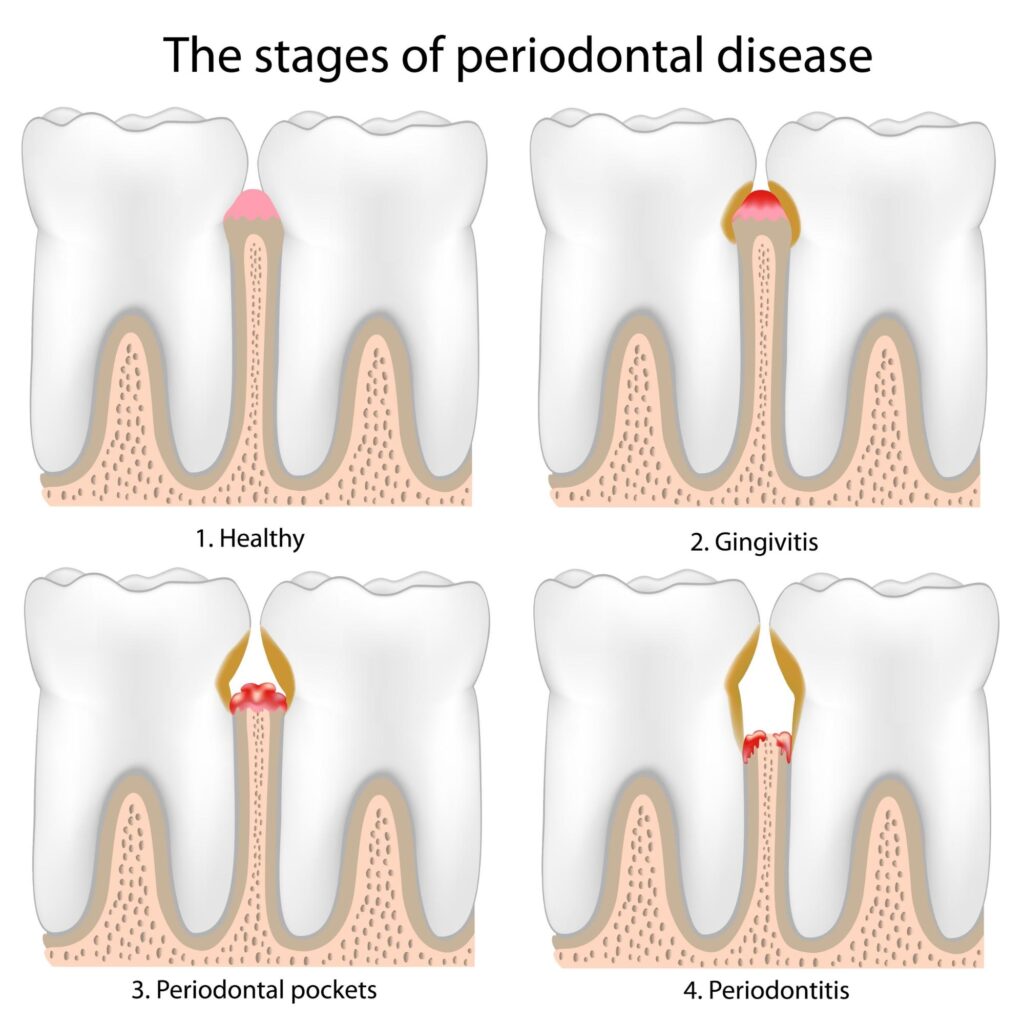
Teeth are not just “stuck” in the gums; they are anchored into the Alveolar Bone by a complex network of fibers called the Periodontal Ligament. Healthy periodontal tissue is as stable as reinforced concrete.
Gum disease occurs when bacteria invade via a “Biofilm,” triggering an immune response. During inflammation, immune cells trying to kill bacteria accidentally damage your own bone tissue. This is not just simple “erosion”; it is a substantial shrinking and disintegration of your dental foundation. When the alveolar bone height drops to a critical point, the tooth becomes like a building on a collapsed foundation—even if the structure (the tooth) is perfect, it will shift, shake, and eventually fall out.
The Culprits: From Plaque to Bacterial Fortresses
The worsening of gum disease is a transition from “soft” to “hard” and from the “surface” to the “core”:
- Bacterial Colonization (Plaque): Within minutes after eating, bacteria form a sticky film on the tooth surface. This is a Biofilm—a protective layer that regular mouthwash cannot penetrate.
- The Mineralization Trap (Calculus): If not removed within 24 hours, plaque absorbs minerals from your saliva and hardens into Calculus (Tartar). Calculus has a rough surface that acts like a magnet for even more bacteria, creating a vicious cycle.
- Penetration and Invasion (Periodontal Pockets): Toxins from calculus cause the gum tissue to pull away from the tooth, creating gaps known as Periodontal Pockets. This is an oxygen-free environment where the most toxic “Anaerobic Bacteria” thrive and multiply.
- Structural Destruction: These deep-seated bacteria directly attack the periodontal ligament and trigger the biological response that destroys bone. Because this happens deep beneath the gum line without significant pain, patients often lose over 50% of their bone support before they even notice their teeth are loose.
Bleeding Gums or Gum Pain? Get Expert Treatment Today!
If you’re experiencing persistent gum issues such as:
- ✅ Bleeding or swollen gums when brushing or flossing
- ✅ Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth
- ✅ Receding gums exposing tooth roots
- ✅ Loose teeth or discomfort while chewing
Our Dental Clinics Offer Comprehensive Gum Disease Treatment, Including:
- 🦷 Deep Cleaning: For early-stage gum disease, we offer thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar.
- 🦷 Scaling and Root Planning: This deep-cleaning procedure removes bacteria from below the gum line and smooths the tooth root to promote healing.
- 🦷 Antibiotic Therapy: We may prescribe antibiotics to control bacterial infection.
- 🦷 Surgical Procedures: For advanced cases, we offer surgical options like flap surgery and bone and tissue grafts, full mouth restorations. We have Periodontal specialists in our team for treating advanced gum disease cases.
Smith & Jain Dentists in Central Hong Kong | Same-Day Appointments Available
2026 Periodontal Treatment Cost Reference
One of the most frequent questions from patients is: “How much does gum disease treatment cost?” or “Is deep cleaning expensive?”
Costs vary depending on the severity of the condition, including the number of teeth affected, whether surgery is required, and whether the case is handled by a General Dentist or a Periodontist (specialist). The following table uses the Private Patient Fee Schedule from The Prince Philip Dental Hospital (PPDH) as a benchmark to help you plan your budget:
Treatment Item | Price Range (HKD) | Remarks |
Non-surgical Periodontal Therapy (per quadrant) | $3,000 – $8,000 | Also known as “Deep Cleaning” or “Root Planing.” The mouth is typically divided into 4 quadrants. |
Periodontal Surgery (per quadrant) | $5,200 – $10,000 | Advanced treatment for deep periodontal pockets (e.g., Flap Surgery). |
Periodontal Regenerative Surgery | $5,000 – $15,000 | Aims to regrow bone. Bone graft material or regenerative membranes are charged separately. |
Managing Peri-implant Biological Complications | $3,000 – $10,000 | Specialized care for inflammation around existing dental implants (Peri-implantitis). |
Periodontal Splinting (per tooth) | $1,000 – $2,000 | Used to stabilize loose teeth and improve chewing stability. |
Supportive Periodontal Care | $500 – $1,500 | Regular follow-ups, maintenance, and specialized cleaning after treatment completion. |
Note: The above prices are for reference only. Actual fees depend on the clinic’s equipment, the doctor’s experience, and the complexity of the case. We recommend consulting your dentist for an accurate quote before starting treatment.

Government vs. Private Dental Care: How Should I Choose?
Many Hong Kong residents ask: “I have gum disease; can’t I just go to a government dental clinic?” In Hong Kong, there is a distinct difference in the scope of services provided:
1. Government Dental Clinics (General Public Sessions)
- Primary Function: To handle emergency dental pain and extractions.
- Gum Disease Handling: If your gum disease has caused severe tooth mobility or infection, the standard procedure at a government clinic is usually Extraction to remove the source of infection.
- Limitations: Due to limited resources, government clinics rarely provide time-consuming, highly technical “Periodontal Preservation Treatments” (such as full-mouth deep cleaning or regenerative surgery).
2. Private Dental Clinics
- Primary Function: Comprehensive oral care and Tooth Preservation.
- Gum Disease Handling: Through staged treatments (Deep Cleaning > Surgery > Long-term Maintenance), private dentists strive to control the infection and stop bone loss so that you can keep your natural teeth.
Conclusion: If your goal is to “save your teeth” and avoid the early need for dentures or implants, seeking a private dentist for complete periodontal therapy is the better choice.

“Regular Scaling” vs. “Deep Cleaning”: What is the Difference?
This is the concept that confuses patients the most. “Why did the doctor say I have gum disease if I get my teeth cleaned regularly?”
Comparison Item | Regular Scaling | Deep Cleaning / Root Planing |
Ideal For | Healthy teeth or mild Gingivitis | Confirmed Periodontitis with deep pockets |
Cleaning Area | Primarily above the gum line | Deep below the gum line (root surface) |
Anesthesia | Usually not required | Often requires Local Anesthesia depending on depth |
Number of Visits | Usually completed in 1 visit | Requires 2–4 visits for the whole mouth due to complexity |
Primary Goal | Remove surface tartar and prevent disease | Scrape away infected tissue from the root to let gums reattach |
Learn about our professional teeth cleaning services ->
A guide to teeth cleaning: process, benefits, and common misconceptions ->
Periodontal Treatment Roadmap
The treatment of gum disease is not a one-time fix but a systematic, step-by-step process. The core objectives are: eliminating the source of infection, reducing periodontal pockets, stabilizing the dental structure, and finally transitioning into long-term maintenance.
Phase 1: Clinical Diagnosis & Risk Assessment
Before commencing any treatment, the dentist must obtain precise data regarding the damage to the periodontal tissues:
- Full-Mouth Periodontal Probing: The dentist uses a periodontal probe to measure the Pocket Depth around every tooth. A depth exceeding 4mm typically indicates inflammation, while a depth over 6mm signifies severe disease.
- Radiographic Assessment: Utilizing full-mouth X-rays (OPG) or Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) to evaluate the vertical and horizontal levels of Alveolar Bone Loss and determine the prognosis of the teeth.
- Analysis of Pathogenic Factors: Assessing the patient’s lifestyle, such as smoking habits, or underlying health conditions like diabetes that may affect the immune system and healing.
Phase 2: Non-Surgical Initial Therapy
This phase is the cornerstone of all periodontal treatments. Over 80% of early to moderate cases can be successfully managed during this stage:
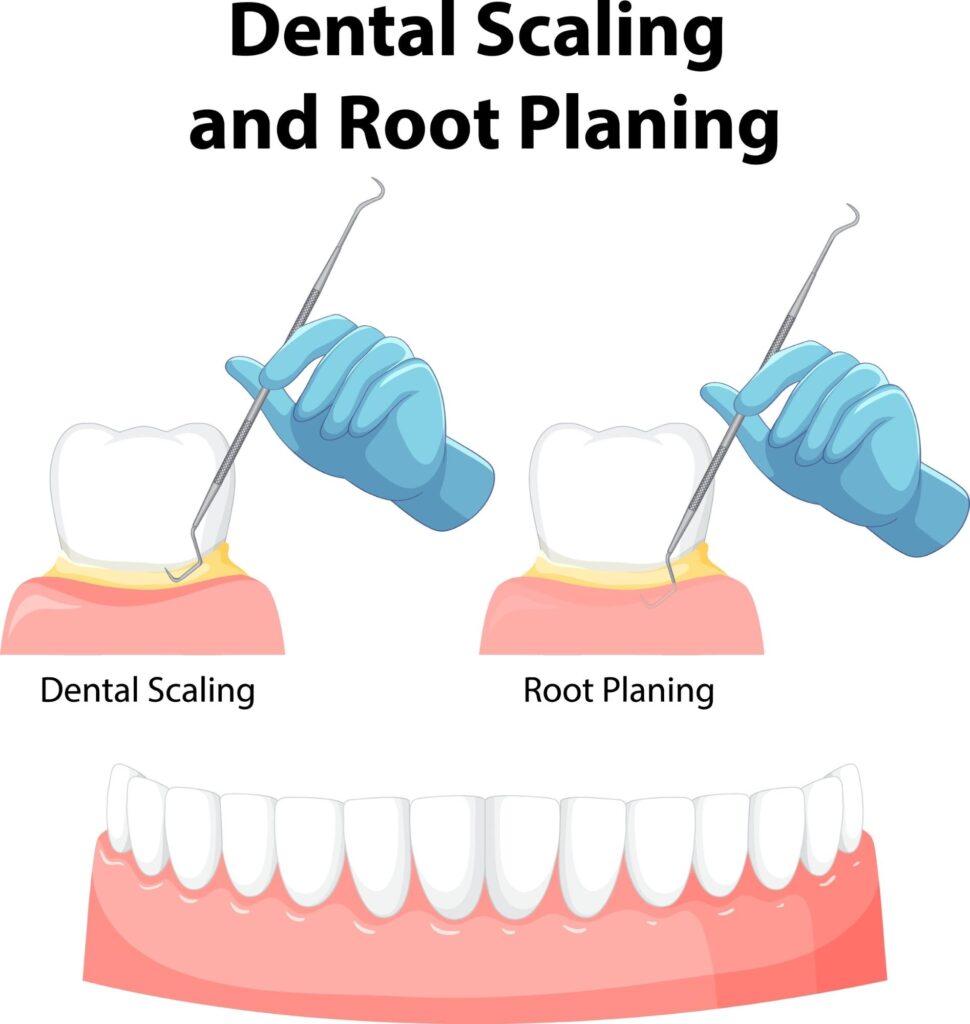
- Scaling & Root Planing (SRP): Performed under local anesthesia, specialized instruments are used to reach deep beneath the gum line. This process thoroughly removes calculus, bacterial biofilms, and infected tissues attached to the root surfaces, smoothing the roots to allow the gums to reattach.
- Biofilm Control Education: Professional guidance on targeted home-care tools, such as interdental brushes or single-tufted brushes. Mastering these tools is the key to ensuring long-term treatment success.
Phase 3: Re-evaluation of Treatment Response
The 6 to 8 weeks following initial therapy are the critical period for tissue healing:
- Healing Indicator Check: Re-measuring pocket depths and the Bleeding on Probing (BOP) index. If pockets have shrunk and bleeding has stopped, the patient can transition to the maintenance phase.
- Determining Next Steps: If pockets deeper than 5-6mm persist with active inflammation, surgical intervention must be considered.
Phase 4: Periodontal Surgical Treatment (Case-Dependent)
When initial therapy cannot fully reach deep-seated bacteria in certain areas, surgery may be required:
- Periodontal Flap Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure where the gum tissue is gently lifted to allow the dentist to perform thorough cleaning under direct vision and reshape irregular bone contours.
- Periodontal Regeneration: For specific bone defects, dentists can implant bone grafts or place Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR) membranes. This stimulates the regrowth of lost periodontal tissues and strengthens the foundation of the tooth.
Phase 5: Supportive Periodontal Care & Maintenance
Gum disease is a chronic condition that can easily recur if bacteria are allowed to accumulate again:
- High-Frequency Follow-ups: Patients in recovery are advised to undergo professional check-ups and cleanings every 3 to 4 months, rather than the traditional six-month interval.
- Long-term Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of gum recession and changes in the bite (occlusion) ensures that treatment results remain stable and extends the functional life of your natural teeth.
How Can You Prevent Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is a condition that can be managed but is difficult to fully cure once damage has occurred. Therefore, prevention is always more critical than treatment. Through consistent home care and regular professional check-ups, you can significantly reduce the risk of the disease occurring or recurring.
Here are the effective prevention methods recommended by dentists 👇
🏠 Home Prevention Habits: Maintaining Healthy Gums Every Day
✅ 1. Correct Brushing Technique (The Bass Method) Brush your teeth at least twice a day (morning and night) for 2–3 minutes each time. The key is “technique” rather than “force.” The Bass Method allows bristles to reach deep into the gum line, effectively removing plaque and preventing gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Recommended Practice:
- Place the toothbrush at a 45° angle to the gums and use a gentle, vibrating back-and-forth motion.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush or an electric toothbrush to avoid damaging the gum tissue.
- Replace your toothbrush every 3 months.
✅ 2. Daily Flossing or Interdental Brushing Brushing alone cannot clean the tight spaces between teeth. Using dental floss or interdental brushes daily effectively removes plaque and food debris hidden between teeth, reducing the chance of gum inflammation.
Interdental Brush Guide: How to Choose and Use It?
✅ 3. Diet and Lifestyle Management
- Reduce sugary and sticky foods: Sugar promotes bacterial growth and accelerates plaque formation.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol: Excessive smoking and alcohol consumption are high-risk factors for periodontal disease, as they reduce blood flow to the gums and impair the body’s healing capabilities.
- Balanced diet: Consume foods rich in Vitamin C (such as kiwis, oranges, and bell peppers) to aid in gum repair and tissue health.
✅ 4. Manage Stress Levels Chronic stress or teeth grinding (bruxism) can indirectly lead to gum recession and periodontal issues. Maintaining good sleep hygiene and moderate exercise helps boost your overall immune system.
🏥 Professional Dental Prevention: Regular Check-ups are Key
✅ 1. Regular Scaling and Dental Exams Even with diligent daily brushing, it is difficult to remove tartar (calculus) hidden below the gum line. We recommend a professional scaling every 6 months to remove tartar from above and below the gums to keep the periodontium clean.
- Note: For high-risk patients (e.g., smokers, diabetics, or those with a history of gum disease), this interval should be shortened to every 3–4 months.
✅ 2. Regular Periodontal Health Assessment Your dentist will track changes in your periodontal health by:
- Measuring Periodontal Pocket Depth (PPD)
- Evaluating the Bleeding on Probing (BOP) index
- Observing gum recession and the condition of the alveolar bone
- This allows for the early detection of potential problems.
✅ 3. Ongoing Oral Hygiene Education Through guidance from your dentist or dental hygienist, learning the brushing techniques and cleaning tools best suited to your specific oral condition is effective for maintaining long-term gum stability.
Bleeding Gums or Gum Pain? Get Expert Treatment Today!
If you’re experiencing persistent gum issues such as:
✅ Bleeding or swollen gums when brushing or flossing
✅ Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth
✅ Receding gums exposing tooth roots
✅ Loose teeth or discomfort while chewing
Our Dental Clinics Offer Comprehensive Gum Disease Treatment, Including:
🦷 Deep Cleaning: For early-stage gum disease, we offer thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar.
🦷 Scaling and Root Planning: This deep-cleaning procedure removes bacteria from below the gum line and smooths the tooth root to promote healing.
🦷 Antibiotic Therapy: We may prescribe antibiotics to control bacterial infection.
🦷 Surgical Procedures: For advanced cases, we offer surgical options like flap surgery and bone and tissue grafts, full mouth restorations. We have Periodontal specialists in our team for treating advanced gum disease cases.
Smith & Jain Dentists in Central Hong Kong | Same-Day Appointments Available
Frequently Asked Questions About Gum Disease
What is gum disease, and how serious is it?
Gum disease (periodontal disease) is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and bones supporting the teeth. It starts with mild gum inflammation (gingivitis) and can progress to severe periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss if untreated.
How do I know if I have gum disease?
Common signs of gum disease include:
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bad breath or a persistent bad taste in the mouth
- Gum recession (teeth appearing longer)
- Loose teeth or widening gaps between teeth
- Pus between teeth and gums
If you notice any of these symptoms, see a dentist as soon as possible.
What causes gum disease?
The primary cause is plaque buildup due to poor oral hygiene. Other risk factors include:
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause)
- Poor diet and nutritional deficiencies
- Stress, which weakens the immune system
- Genetic predisposition
Can gum disease be reversed?
The early stage (gingivitis) can be reversed with good oral hygiene and professional cleanings. However, advanced gum disease (periodontitis) cannot be fully reversed but can be managed with proper treatment.
How is gum disease treated?
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Deep cleaning (Scaling & Root Planing, SRP): Removes plaque and tartar under the gums
- Antibiotics: Used in rinses or gels to control infection
- Laser therapy: Targets infected tissue with minimal discomfort
Surgical Treatments (for severe cases):
- Flap surgery: Removes deep plaque deposits and reshapes bone
- Gum grafting: Restores receded gums
- Bone grafting: Rebuilds bone lost due to infection
Is gum disease painful?
Early gum disease (gingivitis) is usually painless. As it progresses, you may feel gum tenderness, discomfort while eating, or tooth sensitivity. Advanced gum disease can cause pain due to infection and tooth movement.
How often should I see a dentist if I have gum disease?
Patients with gum disease should have professional cleanings every 3 to 4 months instead of the usual 6-month checkups. Your dentist will advise on a suitable schedule based on your condition.
Can gum disease lead to other health problems?
Yes. Research links gum disease to:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Diabetes complications
- Pregnancy risks (preterm birth, low birth weight)
- Respiratory infections
Treating gum disease can help reduce the risk of these health problems.
Does gum disease cause bad breath?
Yes. Bacteria trapped under the gums release toxins that cause persistent bad breath (halitosis). Proper treatment and oral hygiene can help eliminate it.
Can children get gum disease?
Yes, but it is less common. Poor oral hygiene, genetic factors, and medical conditions can contribute to gum disease in children and teenagers.
What happens if gum disease is left untreated?
Untreated gum disease can lead to:
- Chronic bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Tooth loss
- Jawbone deterioration
Can gum disease affect my ability to eat?
Yes. Severe gum disease can cause pain when chewing, loose teeth, and sensitivity, making it difficult to eat certain foods. Treating gum disease early helps prevent these issues.
Can gum disease come back after treatment?
Yes, if oral hygiene is not maintained. Regular dental visits, proper brushing, and flossing can help prevent recurrence.
Disclaimer
All information provided on this website is for informational purposes only and is intended to help readers gain general knowledge about dental health. The content on this website should not be considered a substitute for professional dental diagnosis, advice, or treatment. If you have any dental concerns, please consult a licensed dentist for appropriate medical advice and treatment.
While we strive to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the information provided, we do not guarantee that all content is always up-to-date or applicable to individual circumstances. Smith & Jain Dentists and its affiliates are not responsible for any direct or indirect damages resulting from the use of this website’s information.
This website may include links to external websites for reference purposes only. Smith & Jain Dentists is not responsible for the content or accuracy of third-party websites.