Gum Recession: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Gum recession not only affects your smile but may also lead to tooth sensitivity, periodontal disease, and even tooth loss. This article provides a comprehensive explanation of the causes of gum recession, common symptoms, and high-risk groups. It also introduces treatment options to help you find effective solutions.

What is Gum Recession?
Gum recession, also known as gingival recession, refers to the gradual wearing away or pulling back of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth, exposing more of the tooth or even the root. This condition not only affects the appearance of your smile but also threatens oral health.
When gums recede, “periodontal pockets” form between the gums and teeth. These pockets can accumulate harmful bacteria, and if left untreated, may cause periodontal disease, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss.
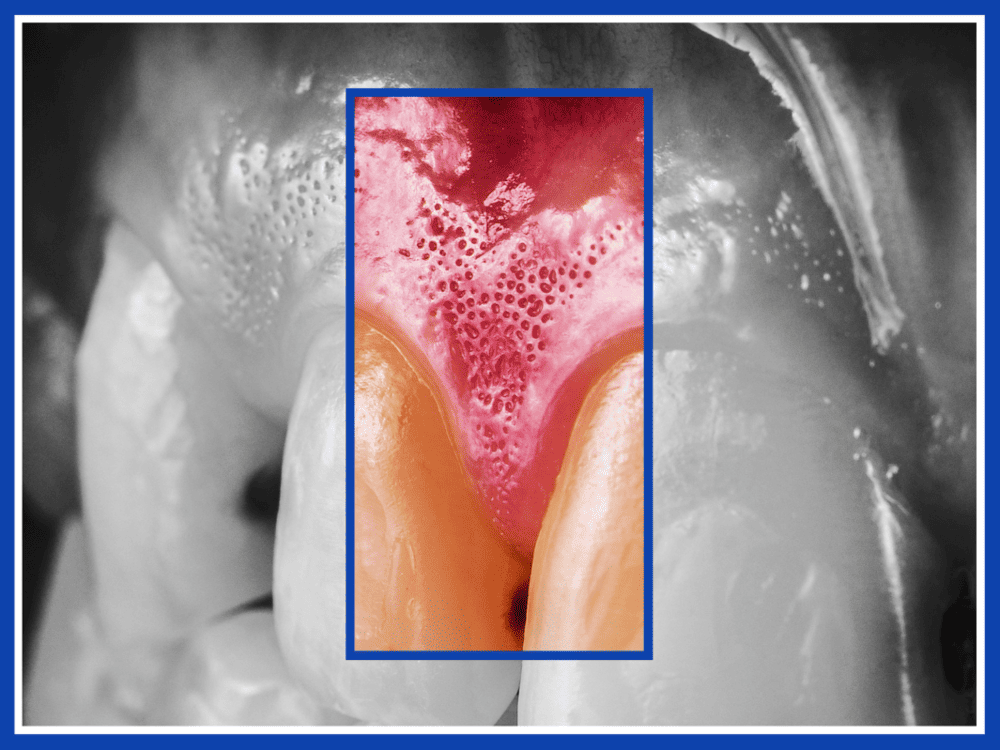
Where are the Gums? (Basic Concept)
The gums are the pink soft tissue in the mouth that surround and protect the teeth. They connect the teeth to the alveolar bone and are one of the most important supporting structures of the teeth. Healthy gums should appear light pink, have a firm texture, and effectively resist bacterial invasion.
Gums are mainly divided into two parts:
- Attached gingiva: Tightly attached to the alveolar bone, providing firm support so that teeth remain stable during chewing.
- Free gingiva: Located at the edge of the tooth, not directly attached to the bone, forming the “gingival sulcus.” Under normal conditions, this groove is shallow, but if deepened by periodontal disease or gum recession, it becomes a place where bacteria accumulate.
👉 Simply put, gums are like the “protective cushion” of your teeth, not only supporting them but also preventing bacteria and external irritation from directly harming the roots and bones.
Safeguard Your Oral Health
At Smith & Jain Dentists, we are committed to delivering professional dental care, from thorough oral examinations to tailored treatments designed for your unique needs. Our expert team provides compassionate guidance throughout your journey to a healthier mouth.
Why Choose Smith & Jain Dentists?
- ✅ Personalized Treatment Plans – Every patient’s oral condition is unique, and we craft targeted solutions to address your specific concerns.
- ✅ Advanced Dental Technology – Utilizing digital diagnostic tools, we ensure precise assessments and effective treatments.
- ✅ Experienced Specialist Team – With extensive expertise, we guarantee top-tier care and swift recovery.
💡 Take the First Step Toward a Pain-Free Mouth! Contact us today to begin your oral health transformation.
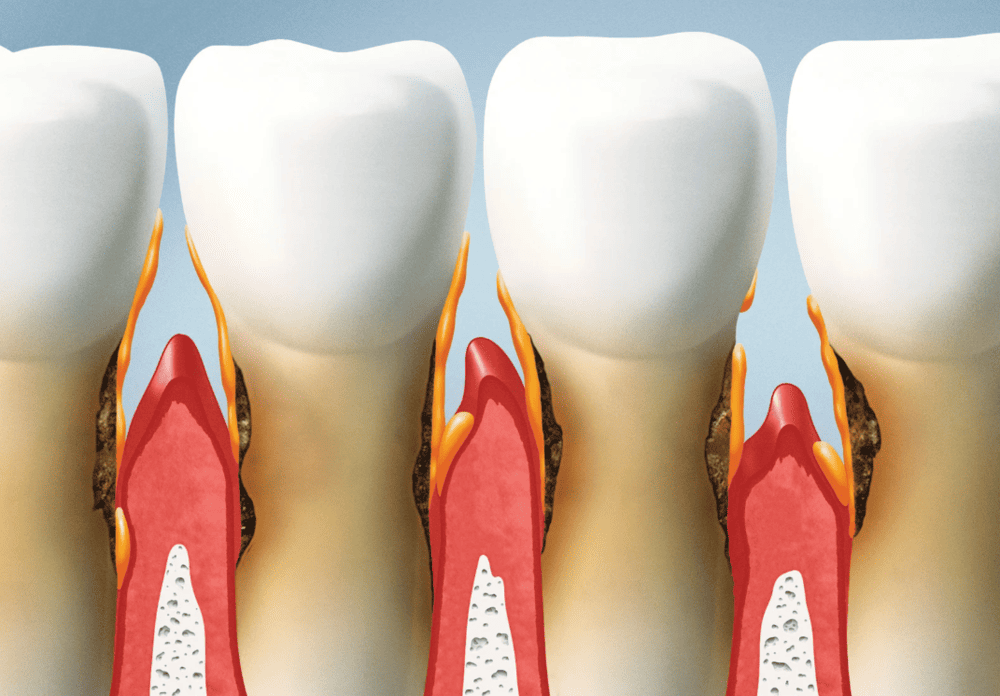
Causes of Gum Recession: Why Are My Gums Receding?
Gum recession does not occur overnight. It is usually the result of long-term influences such as lifestyle habits, oral health issues, and genetic factors. When gum tissue can no longer withstand constant pressure or damage, it gradually recedes, exposing the tooth roots and increasing the risk of tooth sensitivity, periodontal disease, and tooth mobility. The most common causes include:
1. Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush
Many people mistakenly believe that “brushing harder means cleaner teeth,” but in reality, brushing with excessive force or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear down the enamel and continuously irritate the gum margins, eventually leading to gum recession.
2. Poor oral hygiene
Without thorough daily brushing and flossing, dental plaque will continue to accumulate and eventually harden into tartar. Tartar forms at the gumline, causing the gums to gradually become inflamed and recede. This is one of the most common culprits behind gum disease and gum recession.
3. Periodontal disease (gum disease)
The leading cause of gum recession in adults is periodontal disease. When bacteria invade the periodontal tissues, they damage both the gums and the supporting alveolar bone, preventing gums from staying tightly attached to the teeth. This forms “periodontal pockets” and ultimately causes continuous gum recession.
4. Teeth grinding or clenching
Habits such as nighttime bruxism or daytime clenching exert excessive pressure on the gums and tooth roots, accelerating gum wear and even causing cracks or sensitivity.
5. Misaligned teeth or improper bite (malocclusion)
When teeth are crowded or the bite is misaligned, some teeth bear extra force. Over time, this uneven pressure on the gums makes localized gum recession more likely.
6. Orthodontic treatment (braces)
Although braces can improve bite alignment and appearance, the movement of teeth may sometimes cause temporary gum recession. If the patient has naturally thin gums or a history of periodontal disease, the risk is even higher. Always consult a professional dentist for a comprehensive oral examination before starting orthodontic treatment to minimize the risk of gum recession.
7. Trauma or injury
Incorrect brushing technique, oral accidents, or certain dental procedures can also injure the gums locally, leading to recession in that specific area.
8. Genetics and congenital factors
Some people are born with thinner gum tissue or insufficient attachment. Additionally, if there is a family history of periodontal disease, the likelihood of gum recession is higher.
👉 Gum recession is rarely caused by a single factor. It is usually the result of multiple long-term influences. By improving daily habits, maintaining proper oral hygiene, and scheduling regular dental check-ups, most cases of gum recession can be effectively prevented or delayed.
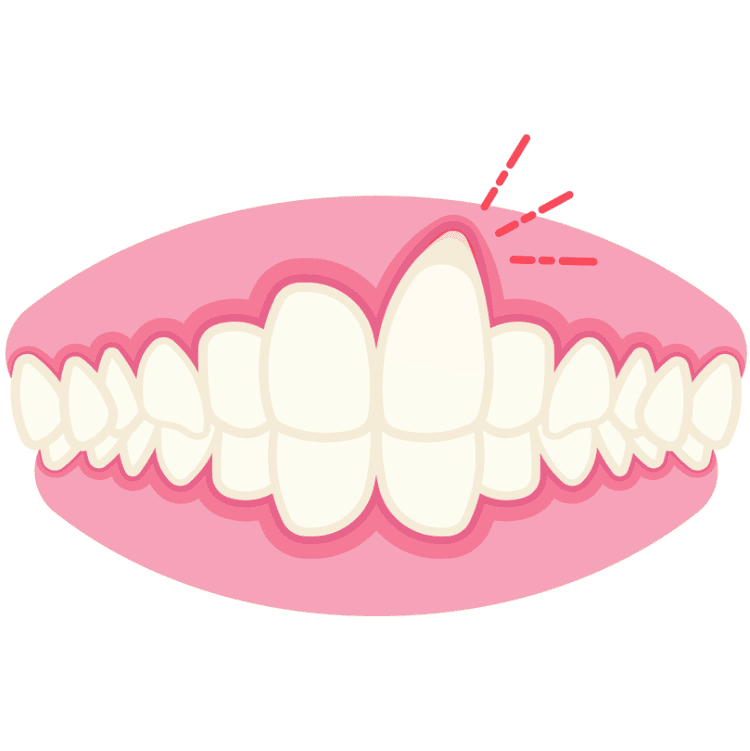
Myths About Gum Recession: Is It Related to Age?
Many people believe that gum recession only happens when you get older, but in reality, it may occur much earlier than you think.
Over 40 years old
Gum recession is most common in this group. As age increases, gum tissue and supporting bone gradually deteriorate. Combined with poor oral hygiene or long-term periodontal disease, gum recession becomes more pronounced.
Over 30 years old
Globally, about half of adults over 30 experience some degree of gum recession. In other words, it is not a rare condition but rather a very common oral health problem.
20s – younger population
Although less common, gum recession can still appear early if there is aggressive tooth brushing, teeth grinding, misaligned teeth, or genetically thinner gums.
👉 Gum recession is not simply a sign of aging. It is closely related to daily habits, periodontal health, bite pressure, and genetic factors. In other words, even young people should not take it lightly. If early symptoms such as receding gum margins, tooth sensitivity, or widening gaps between teeth appear, you should seek examination and correction immediately.
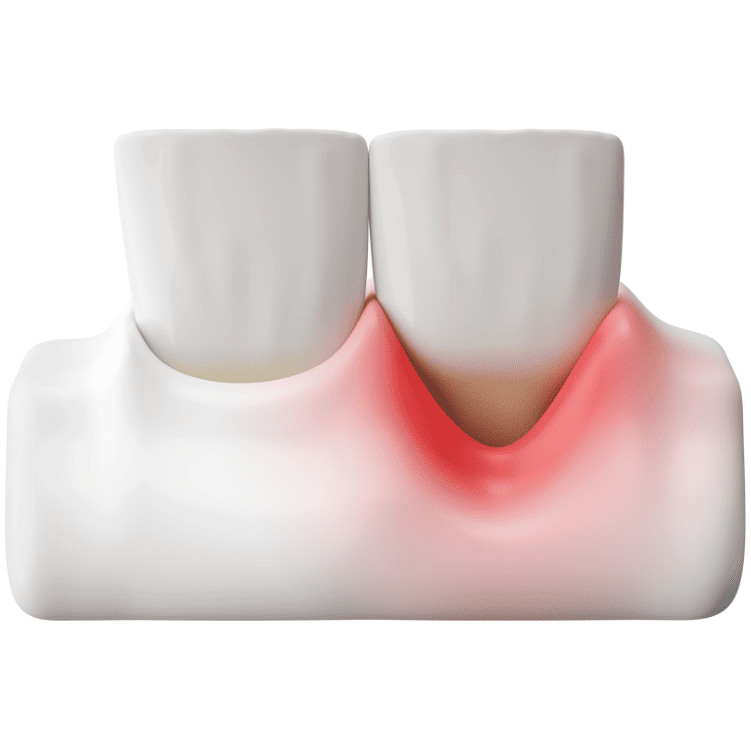
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Recession
Gum recession usually develops gradually and without obvious pain, which is why many people only notice it when the condition becomes more severe. By identifying the warning signs of gum recession early, you can seek treatment sooner, preventing worsening tooth sensitivity, periodontal disease, and even tooth loss.
Here are the common symptoms:
Tooth Sensitivity
After the roots are exposed, the dentin comes into direct contact with the external environment, causing noticeable sensitivity or sharp pain when consuming hot or cold drinks, sweets, or acidic foods.
Teeth Appear Longer
As the gum line gradually recedes, the visible length of the teeth increases, making them look “longer.” This is one of the most intuitive symptoms.
Exposed Roots / Gum Notches
You may see the darker-colored tooth root at the gum edge, or feel a notch or depression with your tongue. This not only affects appearance but also easily accumulates bacteria.
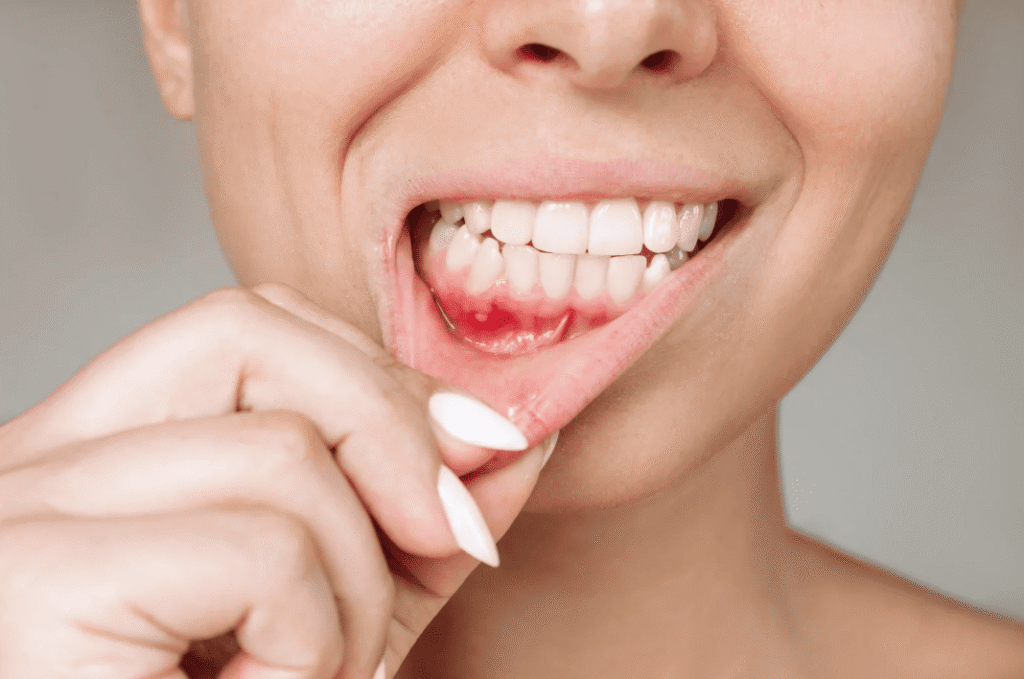
Swollen, Red, or Bleeding Gums
Repeated bleeding while brushing or flossing is a typical sign of gingivitis and early periodontal disease. If ignored, long-term inflammation will accelerate gum recession.
Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Periodontal pockets caused by gum recession easily accumulate bacteria and food debris, producing persistent bad odor that cannot be completely eliminated even after brushing.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
In advanced stages, the supporting strength of the alveolar bone decreases, which may cause teeth to loosen, tilt, or change bite alignment. This is a sign that periodontal disease has seriously affected tooth structure.
👉 Reminder: If you notice any of the above symptoms, it means your gum health is already at risk. Seeking dental consultation, oral examination, and treatment as early as possible can effectively prevent gum recession from worsening and protect your teeth from long-term damage.
Summary of Gum Recession Symptoms
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| 🦷 Tooth Sensitivity | Exposed roots, exposed dentin | Mild to Moderate |
| 👀 Teeth Appear Longer | Gum line recedes, more crown exposed | Moderate |
| 🔍 Exposed Roots / Gum Notches | Gum tissue recession, darker root color, possible depressions | Moderate |
| 💢 Swollen, Red, or Bleeding Gums | Gingivitis, early periodontal disease, bacterial irritation | Mild to Moderate |
| 😮💨 Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis) | Bacteria growth in periodontal pockets, food debris accumulation | Moderate |
| ⚠️ Loose or Shifting Teeth | Advanced periodontal disease, weakened alveolar bone support | Severe |

Can Gum Recession Be Reversed?
The question most patients are most concerned about is: “Will receding gums grow back on their own?” The clear answer is: No. Once gum tissue has receded, it cannot regenerate naturally on its own.
But the good news is that, through professional periodontal treatment and surgical methods, it is possible to effectively stop further deterioration, and in some cases restore gum coverage and function.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession: From Deep Cleaning to Advanced Surgery
Gum recession is not caused by a single factor, so treatment methods vary depending on the degree of recession, periodontal condition, and patient needs. The core goals of treatment are to stop the gums from further recession, improve gum and root protection, and restore oral function and aesthetics.
Dental clinics generally provide both non-surgical treatments and surgical treatments, offering the most suitable solutions for different stages of gum recession.
Non-Surgical Treatments (Suitable for Early to Moderate Stages)
這些治療方法適用於牙肉萎縮尚未嚴重的患者,目的是控制炎症、減少敏感、促進牙齦健康。
1. 深層刮治與牙根平整
- 清除牙齦下的牙菌膜與牙石
- 平整牙根表面,減少細菌附著
- 幫助牙齦重新緊密附著牙根
2. 牙周治療
- 適用於早期牙周病(牙齦炎 / 輕度牙周炎)
- 可降低炎症,防止牙齦繼續受損
- 搭配定期牙周檢查,效果更持久
3. 減敏治療
- 使用專用凝膠、氟化塗層或黏合劑
- 有效降低牙根暴露引起的敏感
- 提升日常飲食的舒適度
手術性治療(適合中期至嚴重)
當牙肉萎縮較明顯,僅靠非手術方式無法改善時,牙周專科醫生可能會建議進行手術治療。
1. 牙齦移植手術
- 從上顎或人工組織取健康牙齦,移植到裸露牙根
- 主要功效:減少牙齒敏感、恢復牙齦線條、保護牙根
- 屬於臨床上最常見且效果穩定的手術方法
2. 再生療法
- 適用於牙齦退縮伴隨骨質流失的患者
- 使用再生膜、骨移植材料或組織刺激蛋白,幫助骨與牙周組織再生
- 能改善牙齒支撐,減少牙齒鬆動風險
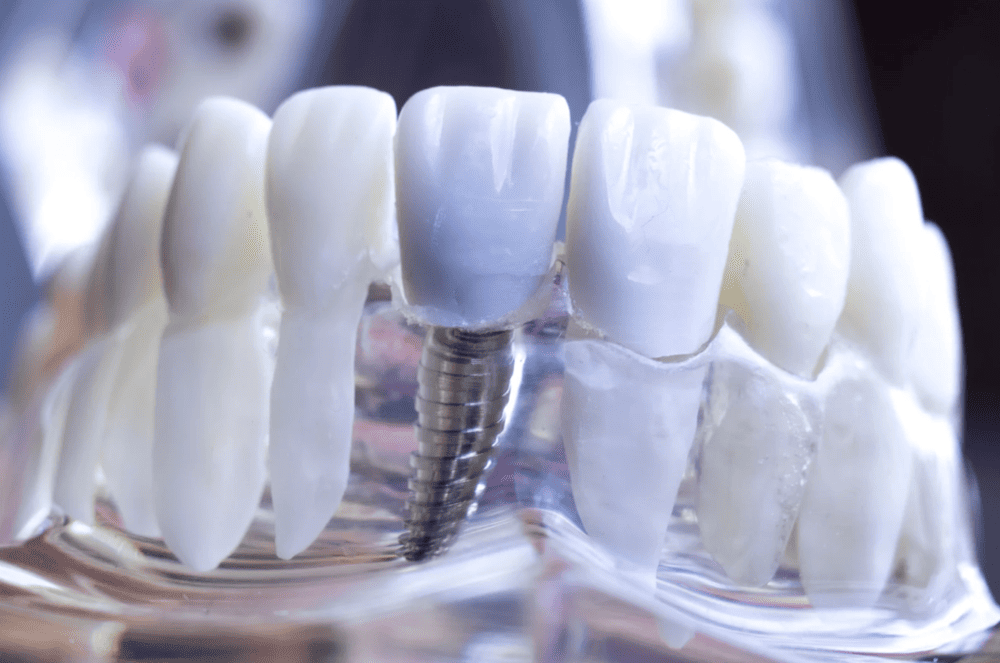
3. 修復性治療
- 適用於牙齦退縮已導致 牙齒缺失的情況
- 選項包括:牙橋、植牙或活動假牙
- 不僅恢復咀嚼功能,也改善笑容美觀
👉 總結來說,牙肉萎縮的治療並非單一模式,而是依照嚴重程度分層進行:
- 早期 → 深層清潔 + 減敏治療
- 中期 → 加上牙周治療,必要時小範圍牙齦移植
- 嚴重 → 再生療法 / 移植手術 / 假牙植牙
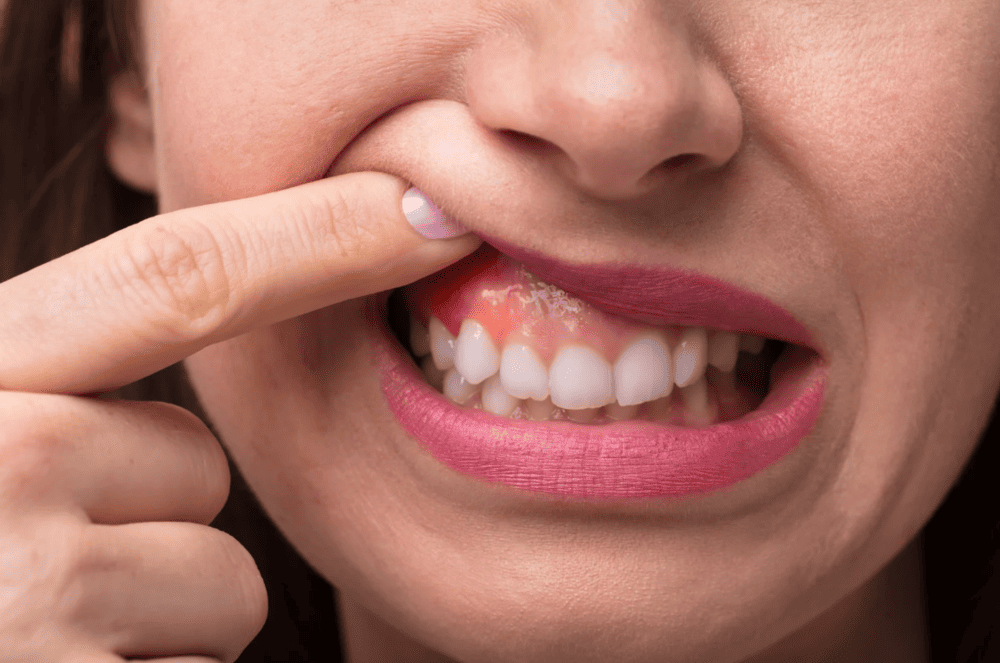
如何預防牙肉萎縮:日常居家護理
透過正確的日常口腔護理,您可以保持牙齦健康、強韌並獲得保護。
✅ 溫和刷牙技巧
使用軟毛牙刷,以小圓圈方式刷牙 — 避免用力來回刷牙,這會磨損牙齦組織。
✅ 每日使用牙線或牙縫刷
清除牙齒間隱藏的牙菌膜與食物殘渣,維持牙齦健康。
✅ 定期牙科檢查
每 6–12 個月安排專業洗牙及牙齦健康檢查(若屬高風險族群,建議每 3–6 個月檢查一次)。
✅ 防止夜間磨牙
若夜間有磨牙或咬牙習慣,可向牙醫諮詢訂製夜間護牙套,減少牙齦與牙齒壓力。
✅ 健康生活習慣
維持均衡飲食,減少糖分攝取,避免過量吸煙或飲酒,降低牙齦疾病風險。
✅ 兒童早期口腔護理習慣
幫助孩子從小養成良好口腔衛生習慣,並定期接受兒童牙科檢查。
守護您的口腔健康!
在 Smith & Jain Dentists,我們提供專業的牙科服務,從口腔檢查到深入治療,訂製適合您的個人化方案。我們的牙醫團隊將全程提供細心指導。
為何選擇 Smith & Jain Dentists?
- ✅ 個人化治療方案 – 每位患者的口腔狀況獨特,我們提供針對性解決方案。
- ✅ 先進牙科科技 – 採用數碼診斷工具,精準評估口腔問題原因,治療更有效。
- ✅ 經驗豐富的專家團隊 – 憑藉專業知識,確保您獲得最佳護理與快速康復。
💡 踏出第一步,邁向健康無痛的口腔!
總結:以健康牙齦守護你的笑容
牙肉萎縮不僅是外觀問題 — 它是牙周病的重要警示信號,若不及早治療,可能引起牙齒敏感、牙槽骨流失,甚至牙齒脫落。越早接受治療,長期效果越好。
👉 不要讓牙肉萎縮奪走你的笑容。透過我們專業的牙科團隊,保護你的牙齦與牙齒健康。
牙肉萎縮常見問題
牙肉萎縮可以自行復原嗎?
很遺憾,不能。雖然非手術療程如深層洗牙和牙周治療可以控制牙周病並減輕症狀,但失去的牙齦組織無法自行再生。
牙齦移植手術會痛嗎?
感謝現代技術及局部麻醉,牙齦移植手術安全且相對舒適。大多數患者僅感到輕微不適,且恢復速度通常很快。
牙肉萎縮治療費用多少?
治療費用視萎縮程度及所需療程而定。專業深層洗牙可能需數千港幣,而牙齦移植手術則費用較高。建議先預約牙醫諮詢,以獲取個人化報價。
牙齦應多久檢查一次?
大部分人每 6–12 個月檢查一次即可。高風險患者(如牙周病病史、吸煙者或糖尿病患者)可能需要每 3–6 個月檢查一次。
停止牙肉萎縮最快的方法是什麼?
最快速的方法是到牙醫診所接受專業洗牙及牙齦健康評估。居家方面,改用溫和刷牙方式、每天使用牙線,並避免吸煙或磨牙等加速牙肉萎縮的習慣。
牙肉萎縮會導致甩牙嗎?
不一定。早期牙肉萎縮可透過專業治療及良好居家護理控制。若牙周病未經治療且嚴重,可能導致牙齒鬆動或脫落。
牙齦移植手術是永久的嗎?
大多數情況下,牙齦移植可以成功覆蓋並保護裸露牙根多年。長期效果取決於維持良好的口腔衛生和定期牙科檢查。
免責聲明
本網站提供的所有資訊僅供參考,旨在幫助讀者獲取有關牙科健康的基本知識。本網站的內容不能替代專業牙醫的診斷、建議或治療。如有牙科問題或疑慮,請務必諮詢持牌牙醫,以獲取適當的醫療建議及治療方案。
本網站已盡力確保資訊的準確性與完整性,但不保證所有內容始終為最新或適用於所有個人情況。Smith & Jain Dentists 及其相關人員不對因使用本網站資訊而引起的任何直接或間接損害負責。
本網站可能包含外部連結,這些連結僅供方便參考,Smith & Jain Dentists 不對第三方網站的內容或其準確性負責。